Demos
py-trees-demo-action-behaviour
A py_trees demo.
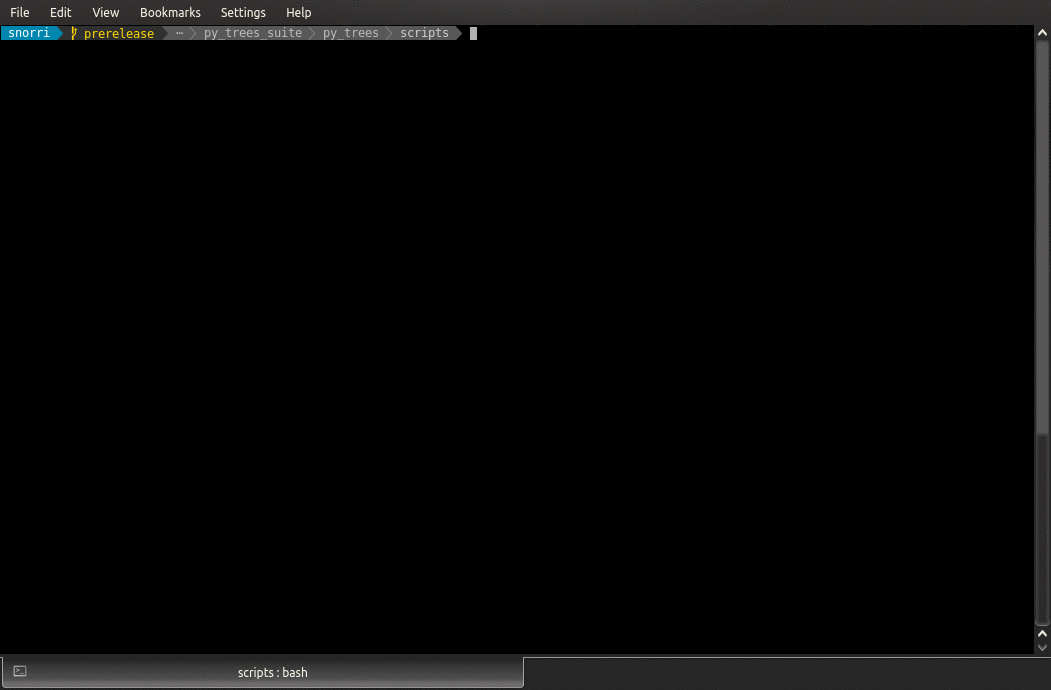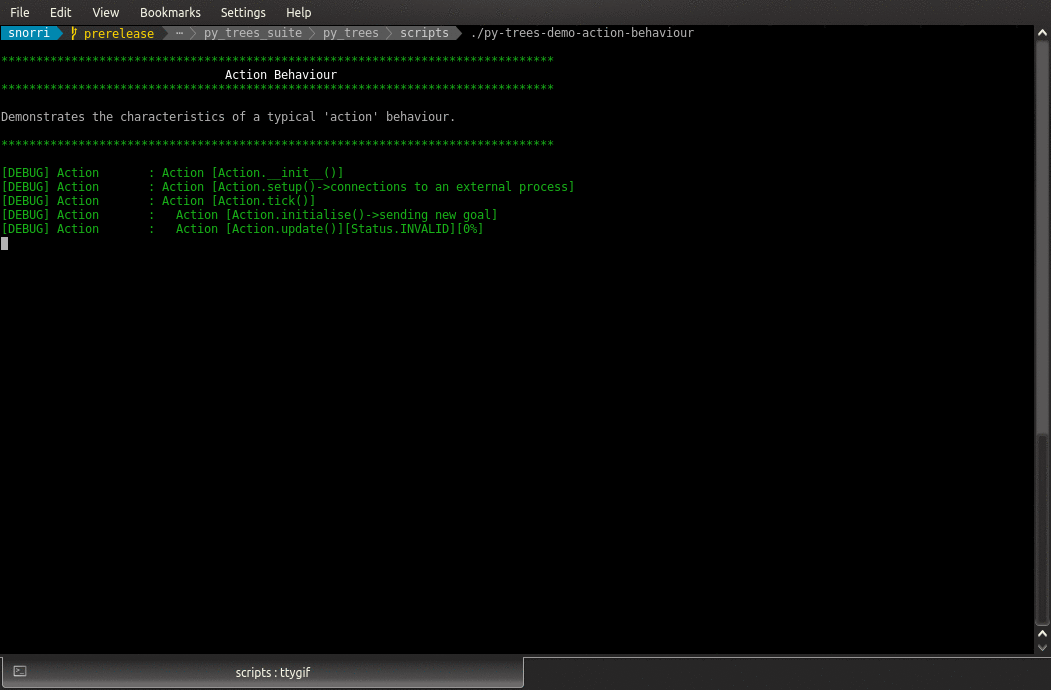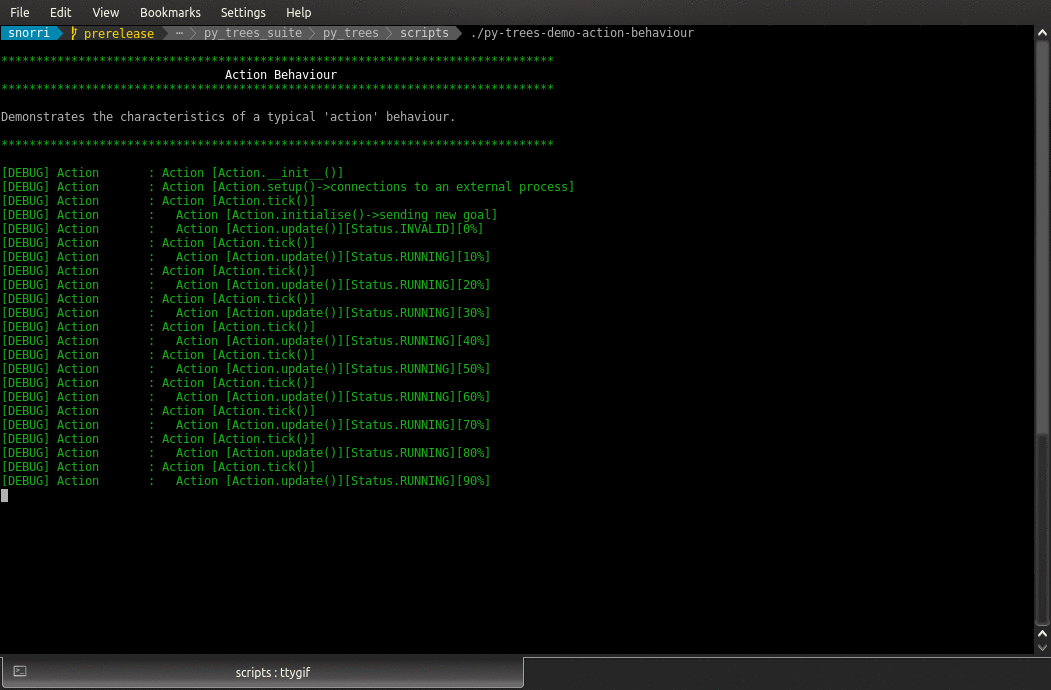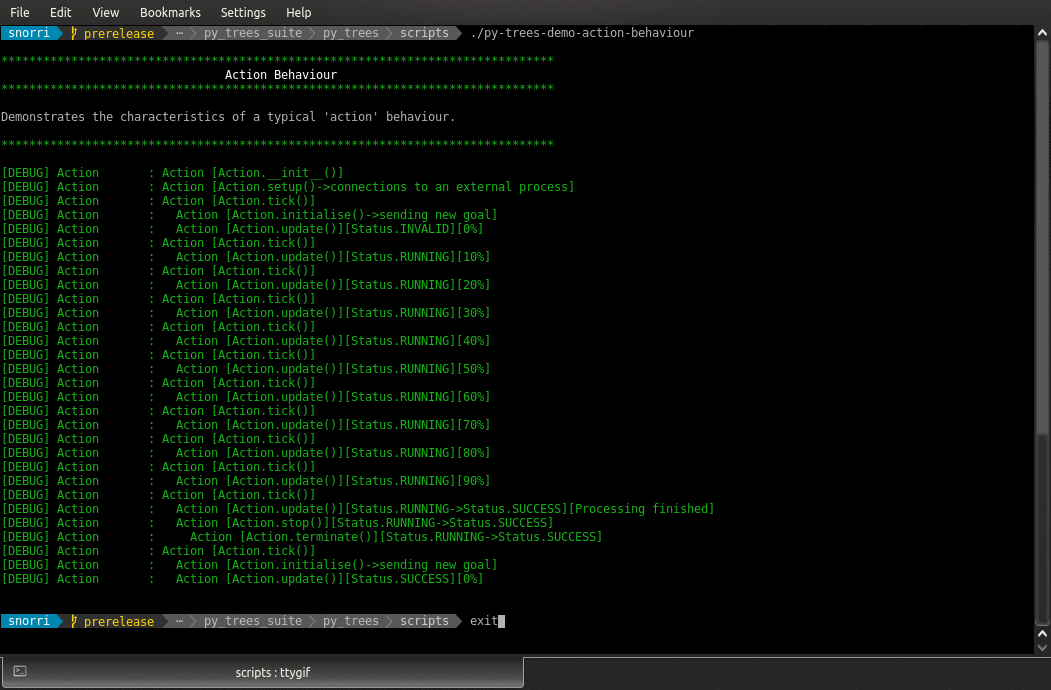
- class py_trees.demos.action.Action(name: str)
Bases:
BehaviourDemonstrates the at-a-distance style action behaviour.
This behaviour connects to a separately running process (initiated in setup()) and proceeeds to work with that subprocess to initiate a task and monitor the progress of that task at each tick until completed. While the task is running the behaviour returns
RUNNING.On completion, the the behaviour returns with success or failure (depending on success or failure of the task itself).
Key point - this behaviour itself should not be doing any work!
- __init__(name: str)
Configure the name of the behaviour.
- initialise() None
Reset a counter variable.
- setup(**kwargs: int) None
Kickstart the separate process this behaviour will work with.
Ordinarily this process will be already running. In this case, setup is usually just responsible for verifying it exists.
- py_trees.demos.action.command_line_argument_parser() ArgumentParser
Process command line arguments.
- Returns:
the argument parser
- py_trees.demos.action.description() str
Print description and usage information about the program.
- Returns:
the program description string
- py_trees.demos.action.epilog() str | None
Print a noodly epilog for –help.
- Returns:
the noodly message
- py_trees.demos.action.main() None
Entry point for the demo script.
- py_trees.demos.action.planning(pipe_connection: Connection) None
Emulate a (potentially) long running external process.
- Args:
pipe_connection: connection to the planning process
py-trees-demo-behaviour-lifecycle
A py_trees demo.
- . argparse::
- module:
py_trees.demos.lifecycle
- func:
command_line_argument_parser
- prog:
py-trees-demo-behaviour-lifecycle
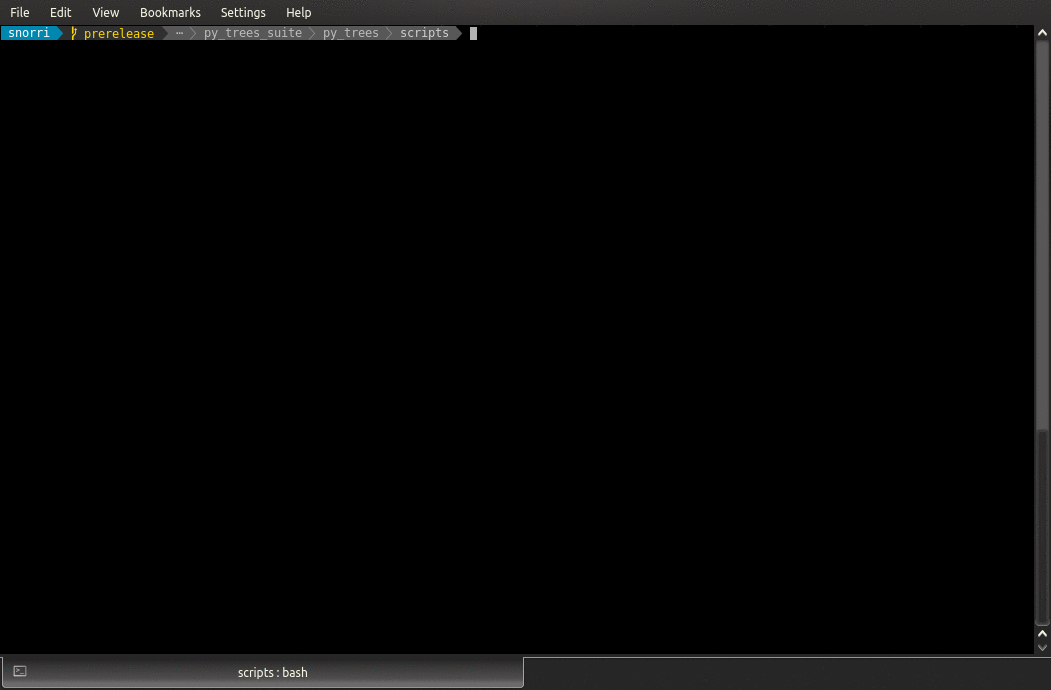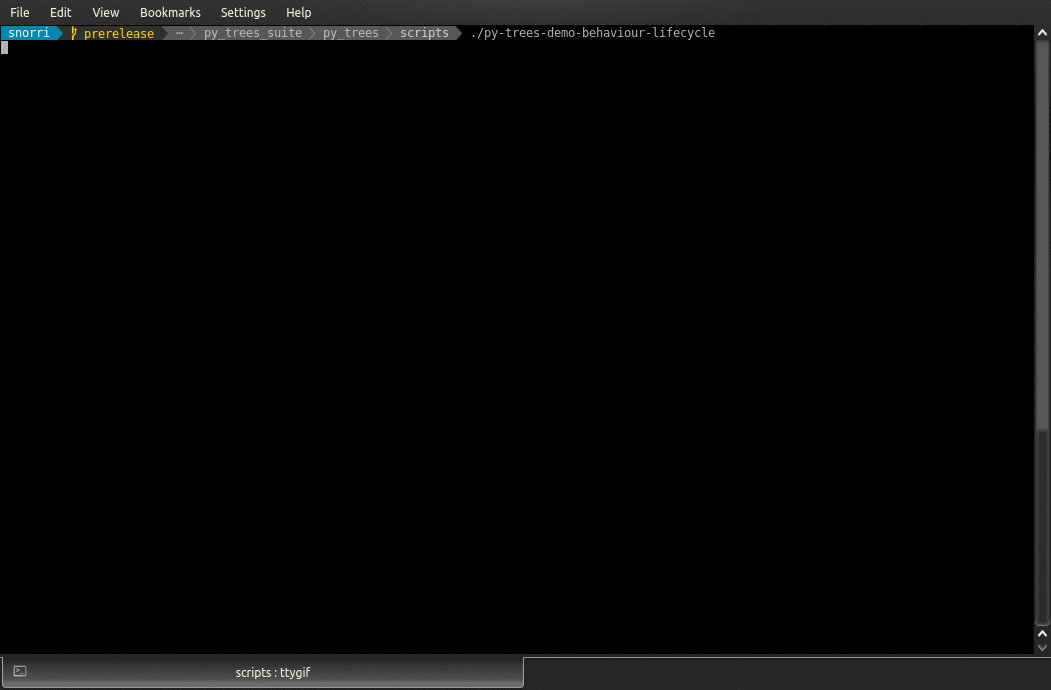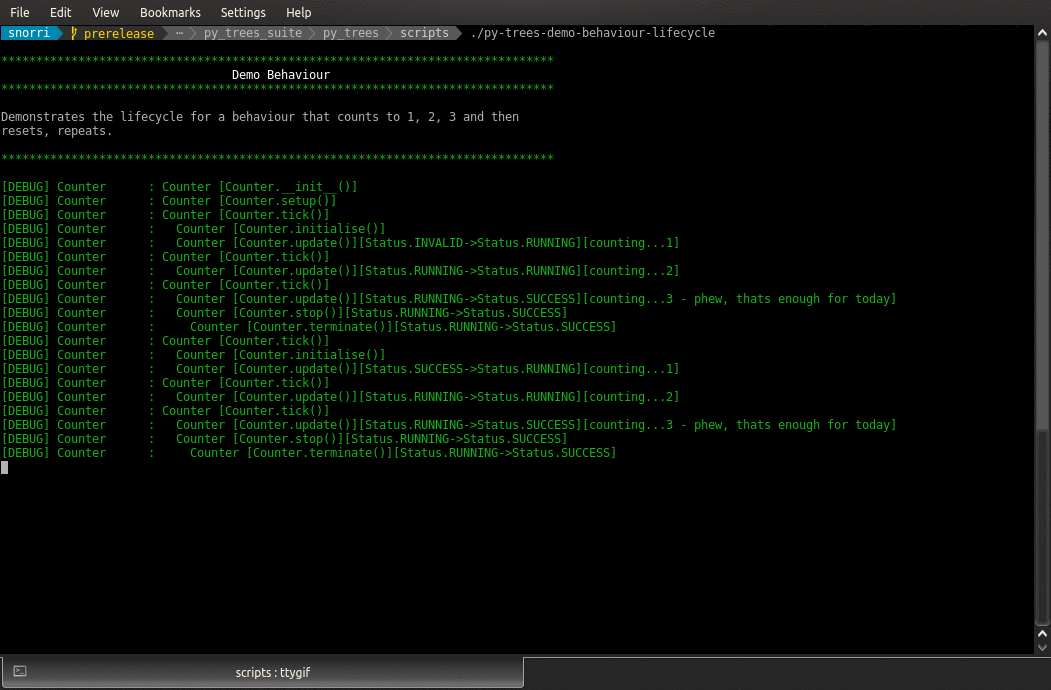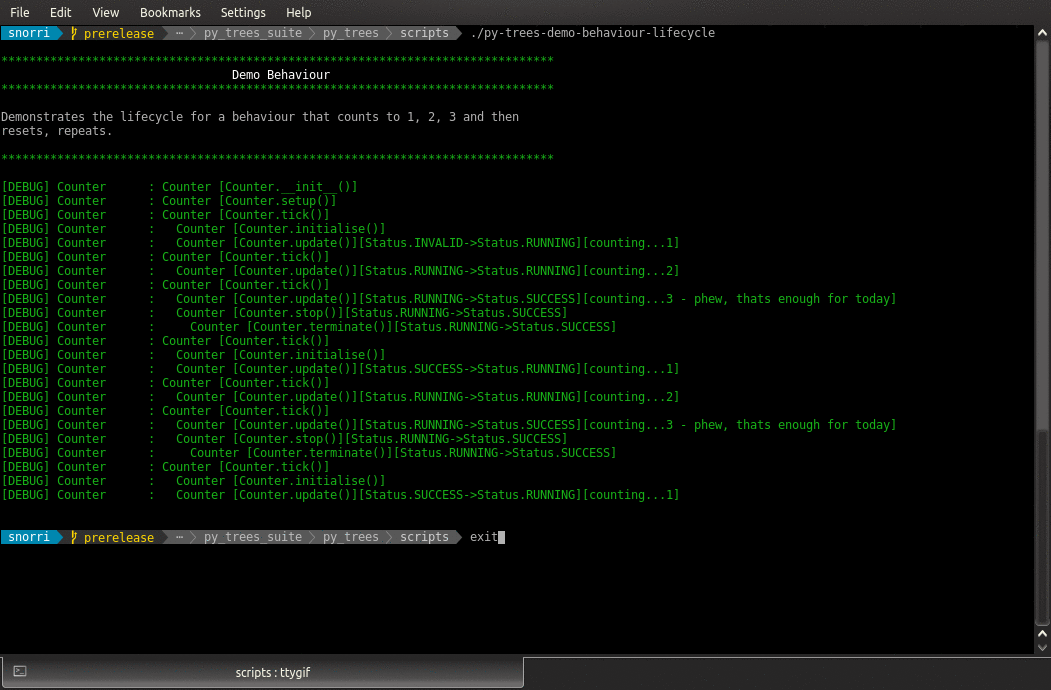
- class py_trees.demos.lifecycle.Counter(name: str = 'Counter')
Bases:
BehaviourSimple counting behaviour.
Increments a counter from zero at each tick
Finishes with success if the counter reaches three
Resets the counter in the initialise() method.
- __init__(name: str = 'Counter')
Configure the name of the behaviour.
- initialise() None
Reset a counter variable.
- setup(**kwargs: int) None
No delayed initialisation required for this example.
- py_trees.demos.lifecycle.command_line_argument_parser() ArgumentParser
Process command line arguments.
- Returns:
the argument parser
- py_trees.demos.lifecycle.description() str
Print description and usage information about the program.
- Returns:
the program description string
- py_trees.demos.lifecycle.epilog() str | None
Print a noodly epilog for –help.
- Returns:
the noodly message
- py_trees.demos.lifecycle.main() None
Entry point for the demo script.
py-trees-demo-blackboard
A py_trees demo.
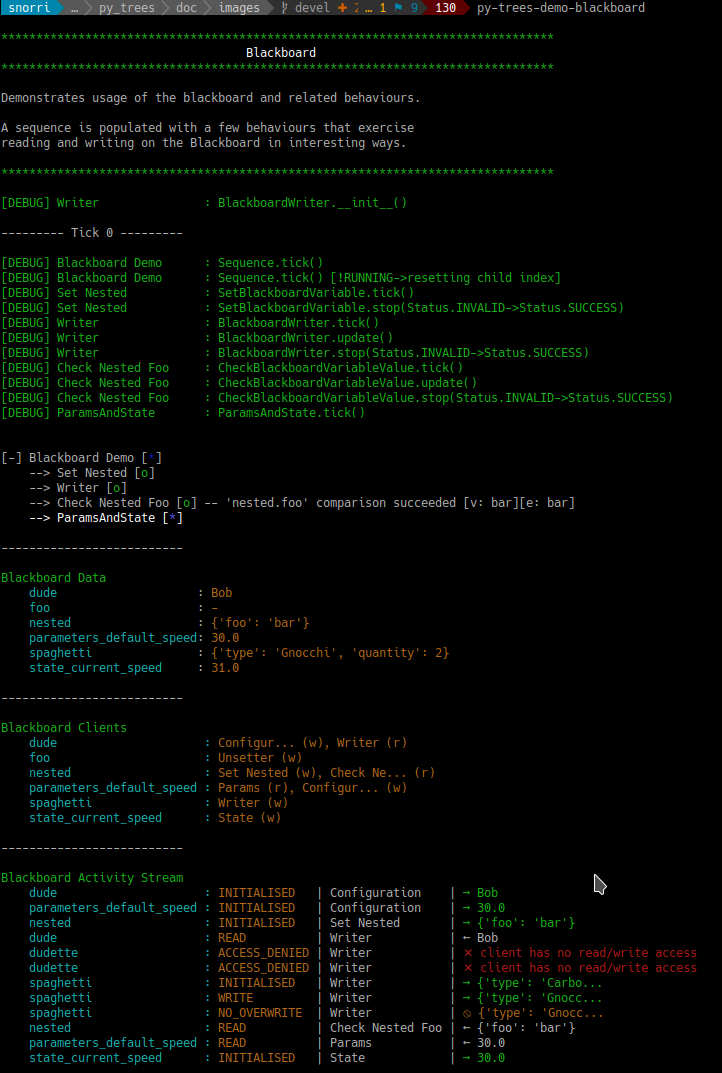
Console Screenshot
- class py_trees.demos.blackboard.BlackboardWriter(name: str)
Bases:
BehaviourWrite some more interesting / complex types to the blacbkoard.
- __init__(name: str)
Set up the blackboard.
- Args:
name: behaviour name
- class py_trees.demos.blackboard.Nested
Bases:
objectA more complex object to interact with on the blackboard.
- __init__() None
Initialise variables to some arbitrary defaults.
- __str__() str
Return str(self).
- __weakref__
list of weak references to the object (if defined)
- class py_trees.demos.blackboard.ParamsAndState(name: str)
Bases:
BehaviourParameter and state storage on the blackboard.
This behaviour demonstrates the usage of namespaces and multiple clients to perform getting and setting of parameters and state in a concise and convenient manner.
- __init__(name: str)
Set up separate blackboard clients for parameters and state.
- Args:
name: behaviour name
- initialise() None
Initialise speed from the stored parameter variable on the blackboard.
- py_trees.demos.blackboard.command_line_argument_parser() ArgumentParser
Process command line arguments.
- Returns:
the argument parser
- py_trees.demos.blackboard.create_root() Behaviour
Create the root behaviour and it’s subtree.
- Returns:
the root behaviour
- py_trees.demos.blackboard.description() str
Print description and usage information about the program.
- Returns:
the program description string
- py_trees.demos.blackboard.epilog() str | None
Print a noodly epilog for –help.
- Returns:
the noodly message
- py_trees.demos.blackboard.main() None
Entry point for the demo script.
py-trees-demo-blackboard-namespaces
A py_trees demo.

Console Screenshot
- py_trees.demos.blackboard_namespaces.command_line_argument_parser() ArgumentParser
Process command line arguments.
- Returns:
the argument parser
- py_trees.demos.blackboard_namespaces.description() str
Print description and usage information about the program.
- Returns:
the program description string
- py_trees.demos.blackboard_namespaces.epilog() str | None
Print a noodly epilog for –help.
- Returns:
the noodly message
- py_trees.demos.blackboard_namespaces.main() None
Entry point for the demo script.
py-trees-demo-blackboard-remappings
A py_trees demo.
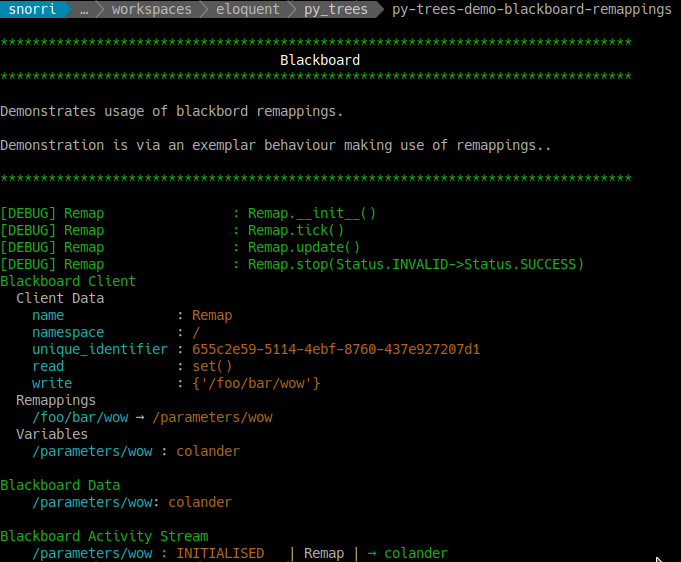
Console Screenshot
- class py_trees.demos.blackboard_remappings.Remap(name: str, remap_to: Dict[str, str])
Bases:
BehaviourCustom writer that submits a more complicated variable to the blackboard.
- __init__(name: str, remap_to: Dict[str, str])
Set up the blackboard and remap variables.
- Args:
name: behaviour name remap_to: remappings (from variable name to variable name)
- py_trees.demos.blackboard_remappings.command_line_argument_parser() ArgumentParser
Process command line arguments.
- Returns:
the argument parser
- py_trees.demos.blackboard_remappings.description() str
Print description and usage information about the program.
- Returns:
the program description string
- py_trees.demos.blackboard_remappings.epilog() str | None
Print a noodly epilog for –help.
- Returns:
the noodly message
- py_trees.demos.blackboard_remappings.main() None
Entry point for the demo script.
py-trees-demo-context-switching
A py_trees demo.
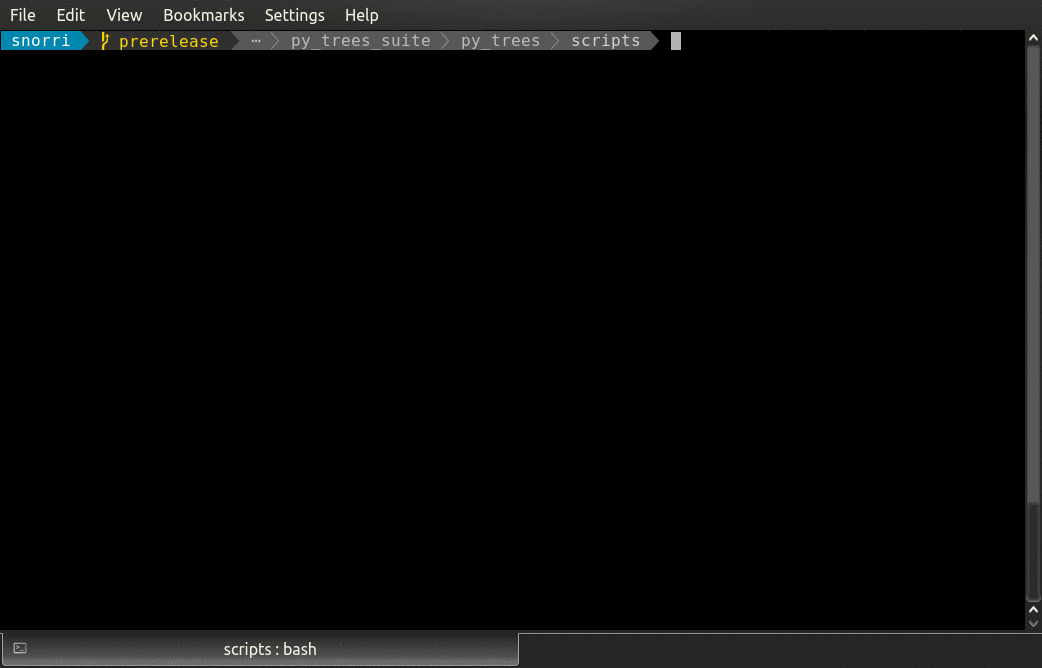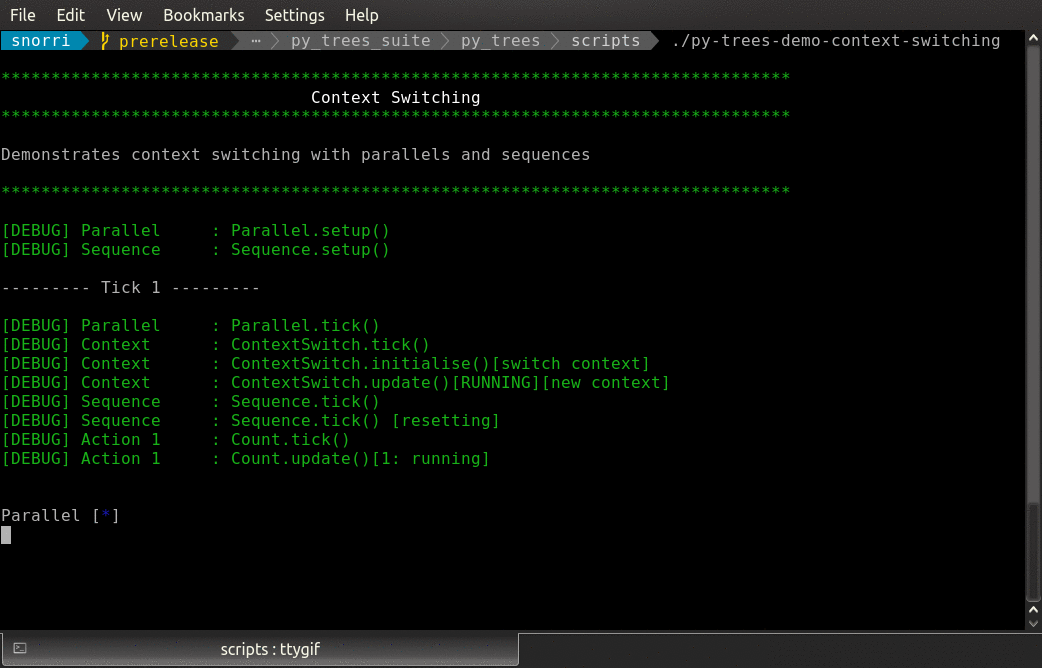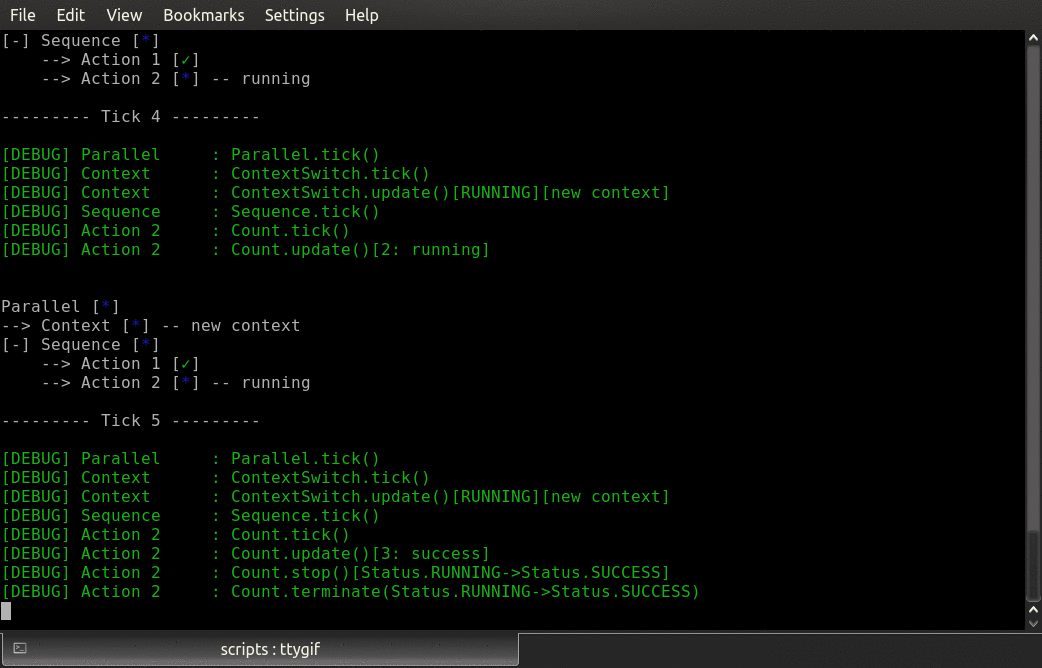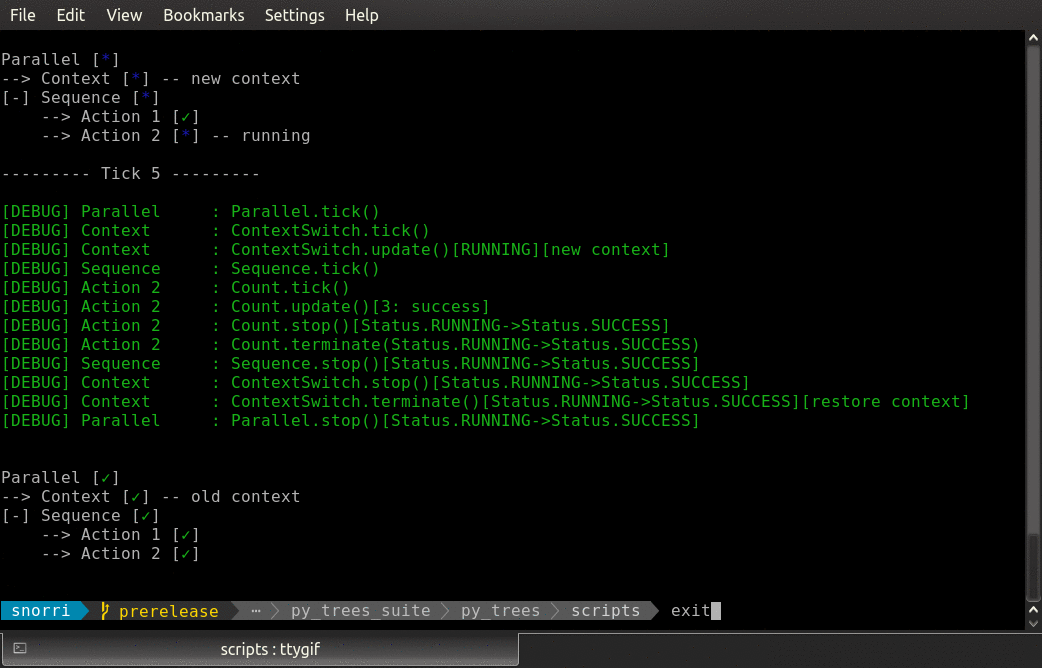
- class py_trees.demos.context_switching.ContextSwitch(name: str = 'ContextSwitch')
Bases:
BehaviourAn example of a context switching class.
This class sets (in
initialise()) and restores a context (interminate()). Use in parallel with a sequence/subtree that does the work while in this context.Attention
Simply setting a pair of behaviours (set and reset context) on either end of a sequence will not suffice for context switching. In the case that one of the work behaviours in the sequence fails, the final reset context switch will never trigger.
- __init__(name: str = 'ContextSwitch')
Initialise with a behaviour name.
- initialise() None
Backup and set a new context.
- py_trees.demos.context_switching.command_line_argument_parser() ArgumentParser
Process command line arguments.
- Returns:
the argument parser
- py_trees.demos.context_switching.create_root() Behaviour
Create the root behaviour and it’s subtree.
- Returns:
the root behaviour
- py_trees.demos.context_switching.description() str
Print description and usage information about the program.
- Returns:
the program description string
- py_trees.demos.context_switching.epilog() str | None
Print a noodly epilog for –help.
- Returns:
the noodly message
- py_trees.demos.context_switching.main() None
Entry point for the demo script.
py-trees-demo-dot-graphs
A py_trees demo.
- py_trees.demos.dot_graphs.command_line_argument_parser() ArgumentParser
Process command line arguments.
- Returns:
the argument parser
- py_trees.demos.dot_graphs.create_tree(level: str) Behaviour
Create the root behaviour and it’s subtree.
- Returns:
the root behaviour
- py_trees.demos.dot_graphs.description() str
Print description and usage information about the program.
- Returns:
the program description string
- py_trees.demos.dot_graphs.epilog() str | None
Print a noodly epilog for –help.
- Returns:
the noodly message
- py_trees.demos.dot_graphs.main() None
Entry point for the demo script.
py-trees-demo-either-or
A py_trees demo.
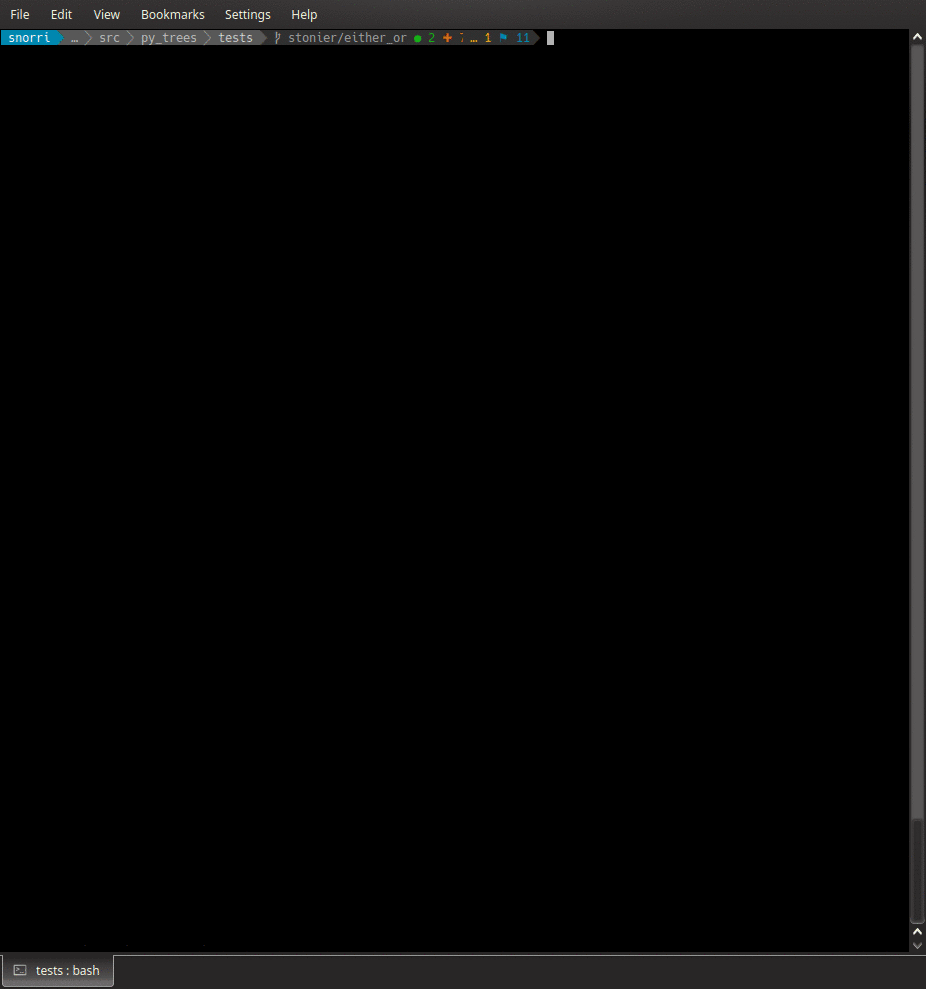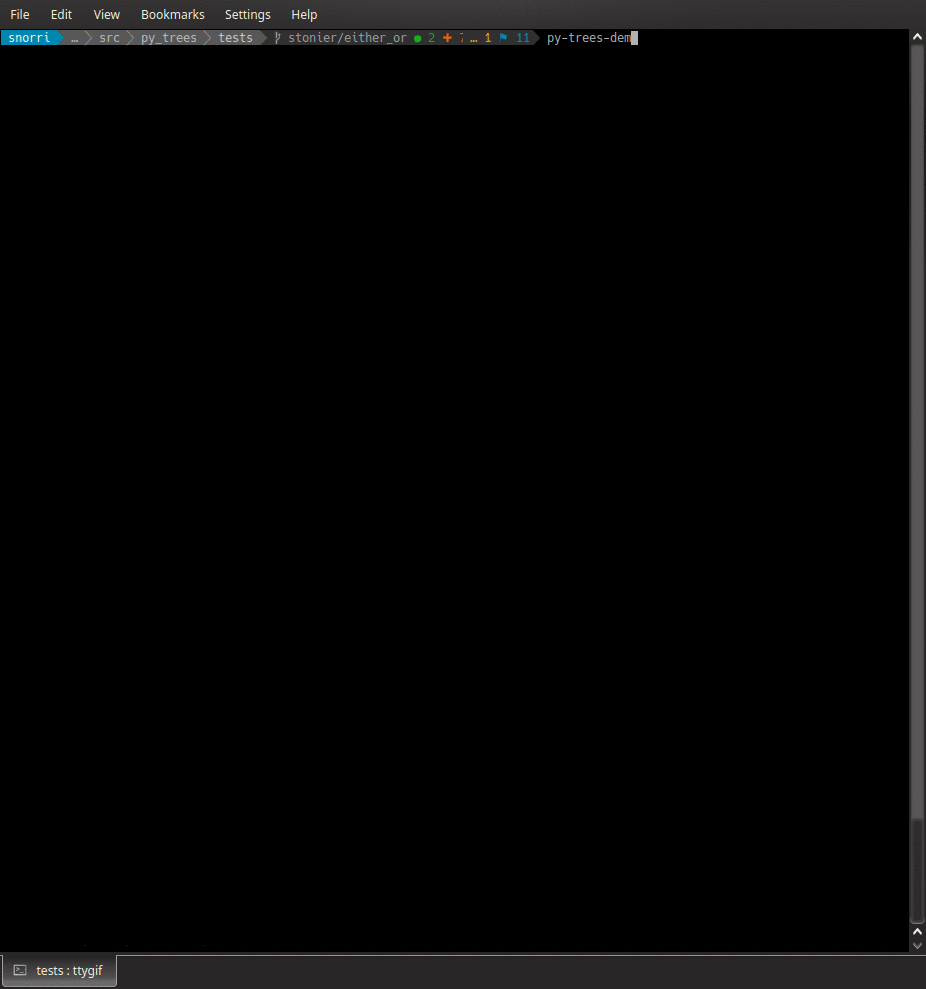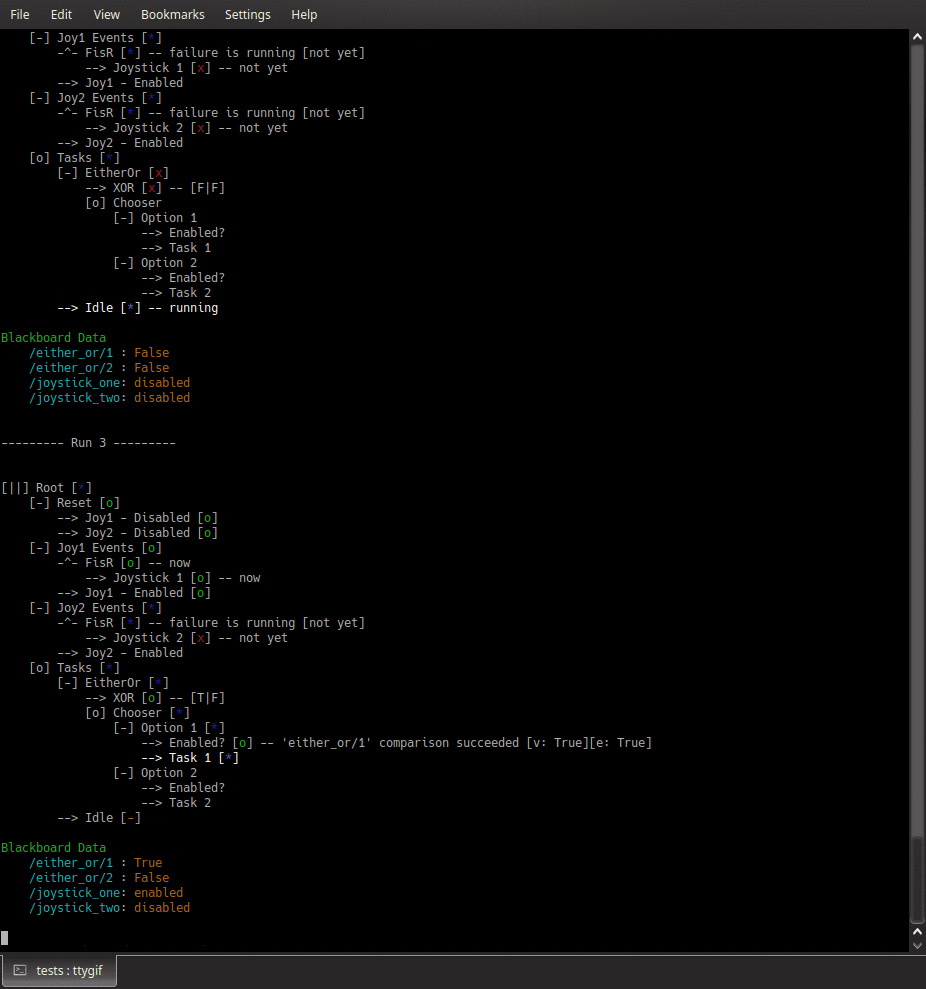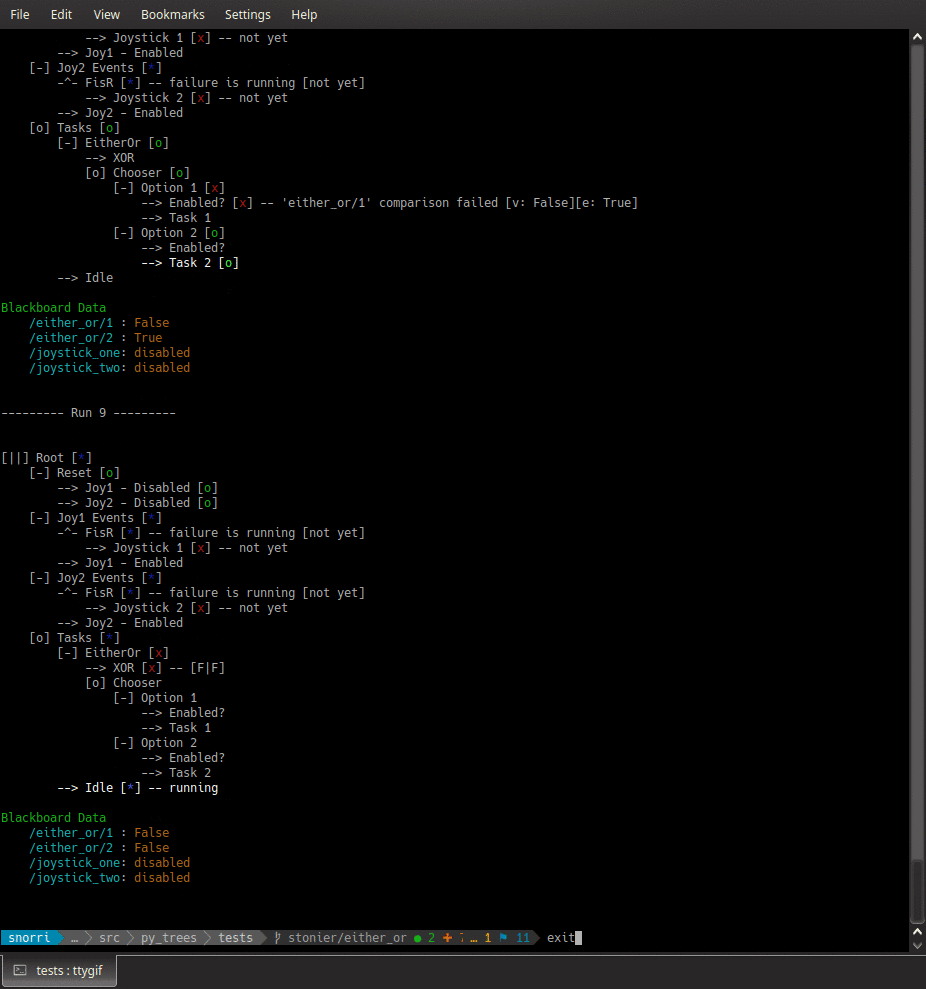
- py_trees.demos.either_or.command_line_argument_parser() ArgumentParser
Process command line arguments.
- Returns:
the argument parser
- py_trees.demos.either_or.create_root() Behaviour
Create the root behaviour and it’s subtree.
- Returns:
the root behaviour
- py_trees.demos.either_or.description(root: Behaviour) str
Print description and usage information about the program.
- Returns:
the program description string
- py_trees.demos.either_or.epilog() str | None
Print a noodly epilog for –help.
- Returns:
the noodly message
- py_trees.demos.either_or.main() None
Entry point for the demo script.
- py_trees.demos.either_or.post_tick_handler(snapshot_visitor: SnapshotVisitor, behaviour_tree: BehaviourTree) None
Print data about the part of the tree visited.
- Args:
snapshot_handler: gather data about the part of the tree visited behaviour_tree: tree to gather data from
- py_trees.demos.either_or.pre_tick_handler(behaviour_tree: BehaviourTree) None
Print a banner with current tick count prior to ticking the tree.
- Args:
behaviour_tree: the tree to tick (used to fetch the count number)
py-trees-demo-eternal-guard
A py_trees demo.
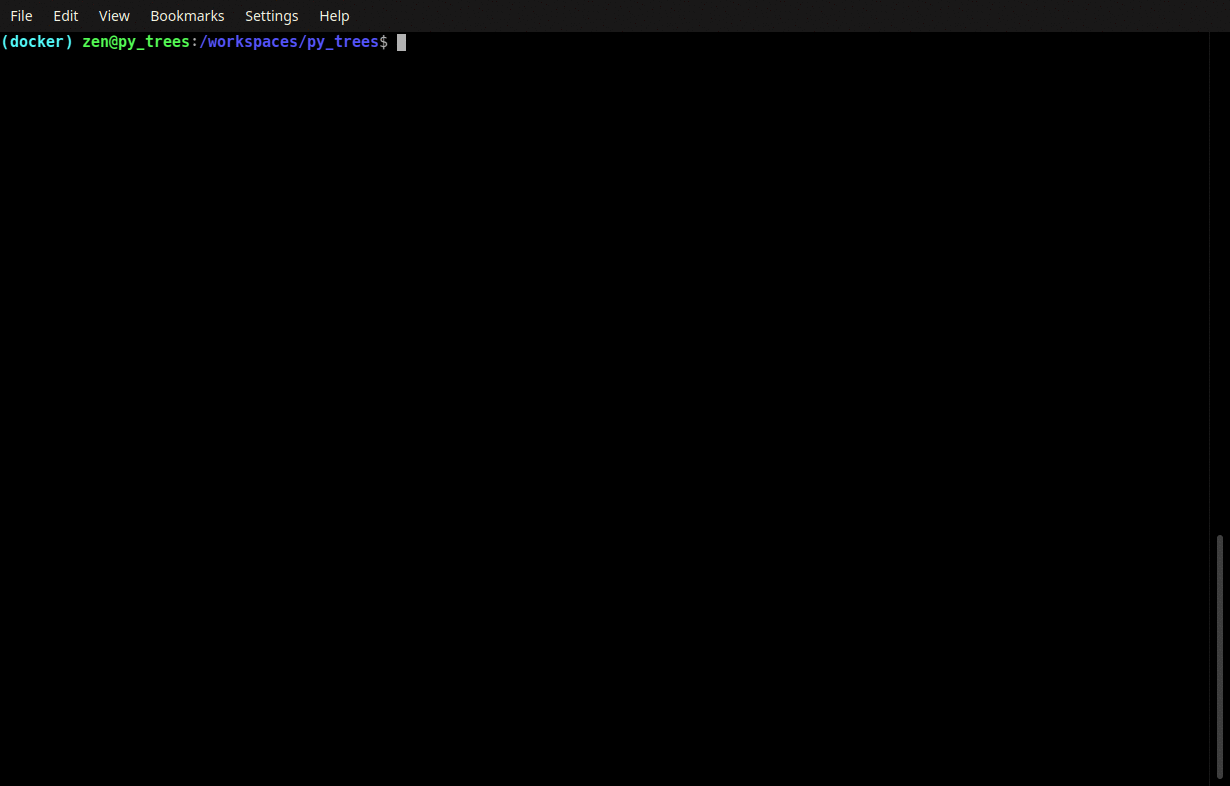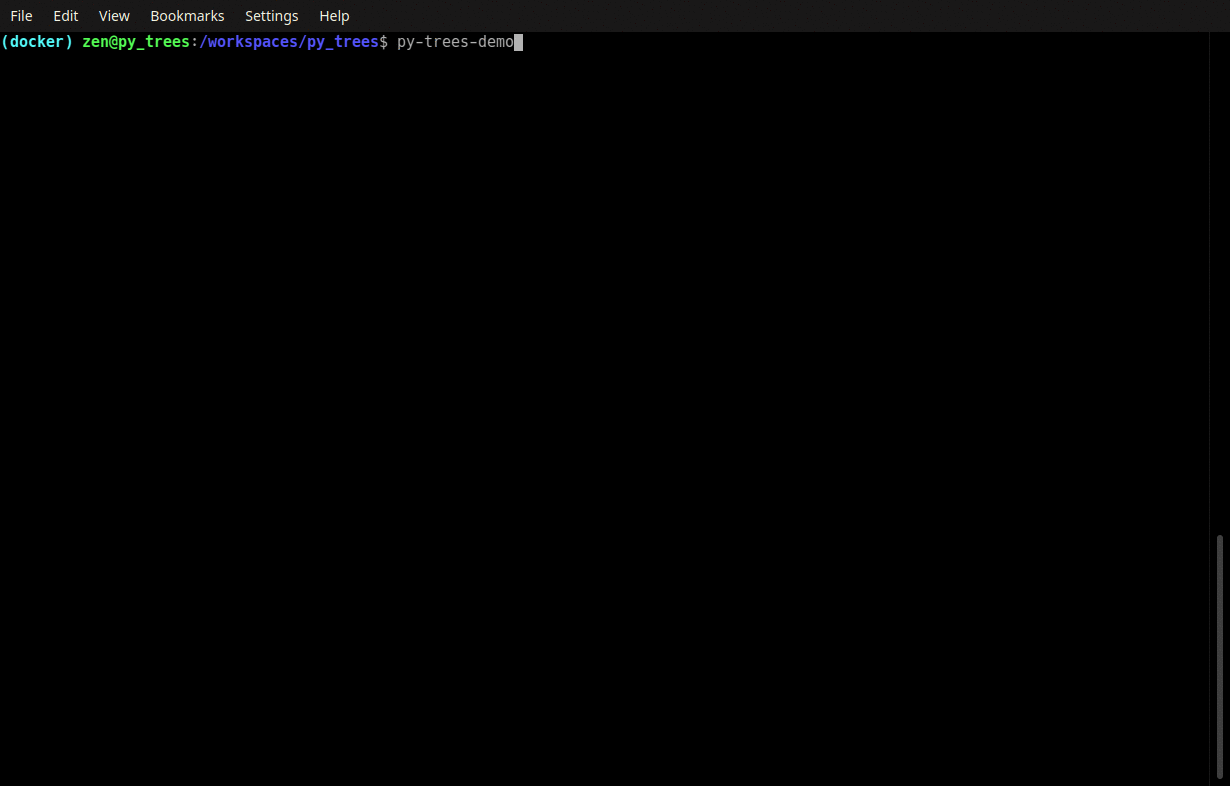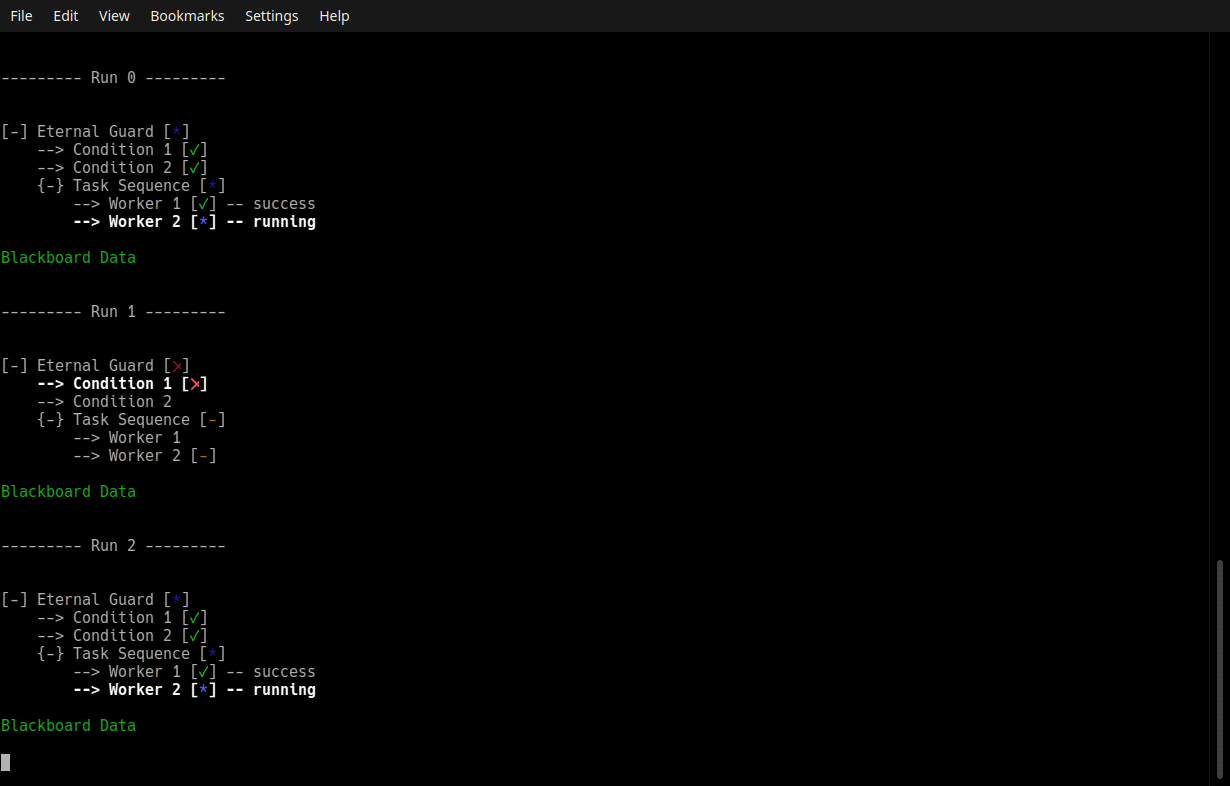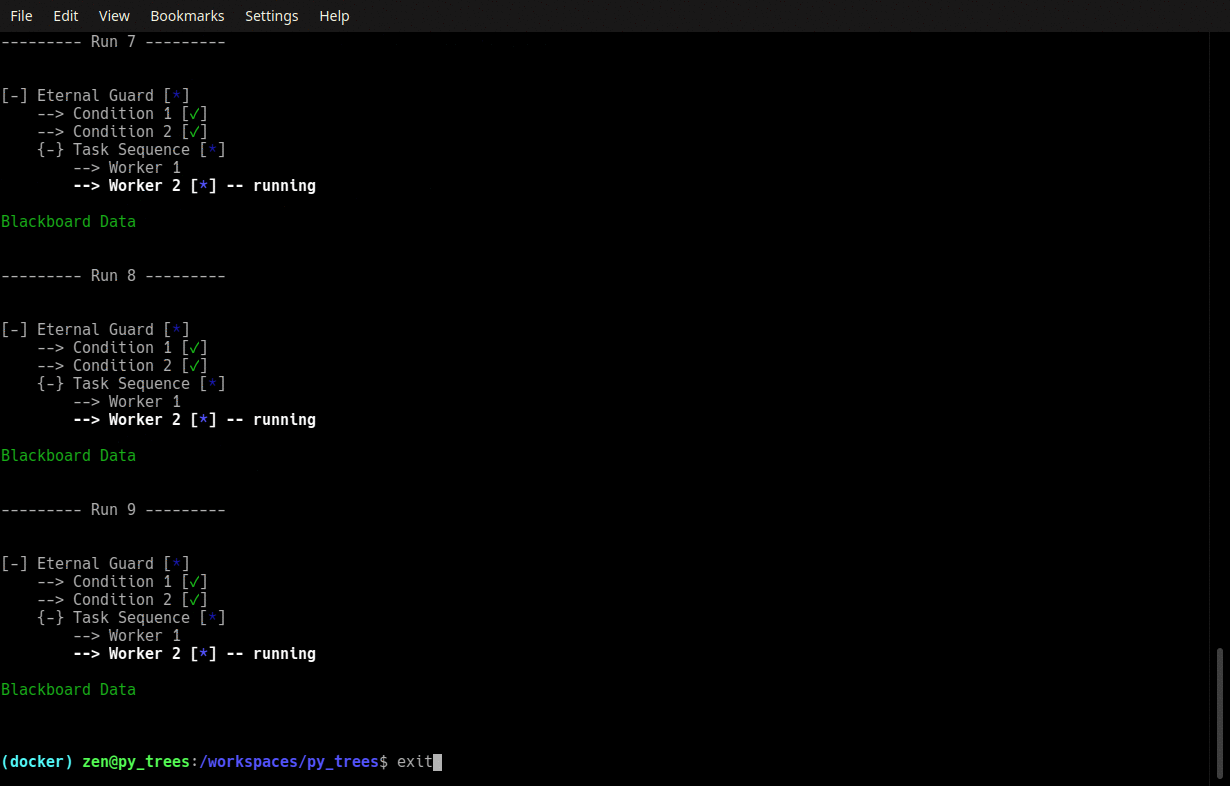
- py_trees.demos.eternal_guard.command_line_argument_parser() ArgumentParser
Process command line arguments.
- Returns:
the argument parser
- py_trees.demos.eternal_guard.create_root() Behaviour
Create the root behaviour and it’s subtree.
- Returns:
the root behaviour
- py_trees.demos.eternal_guard.description(root: Behaviour) str
Print description and usage information about the program.
- Returns:
the program description string
- py_trees.demos.eternal_guard.epilog() str | None
Print a noodly epilog for –help.
- Returns:
the noodly message
- py_trees.demos.eternal_guard.main() None
Entry point for the demo script.
- py_trees.demos.eternal_guard.post_tick_handler(snapshot_visitor: SnapshotVisitor, behaviour_tree: BehaviourTree) None
Print data about the part of the tree visited.
- Args:
snapshot_handler: gather data about the part of the tree visited behaviour_tree: tree to gather data from
- py_trees.demos.eternal_guard.pre_tick_handler(behaviour_tree: BehaviourTree) None
Print a banner with current tick count prior to ticking the tree.
- Args:
behaviour_tree: the tree to tick (used to fetch the count number)
py-trees-demo-logging
A py_trees demo.
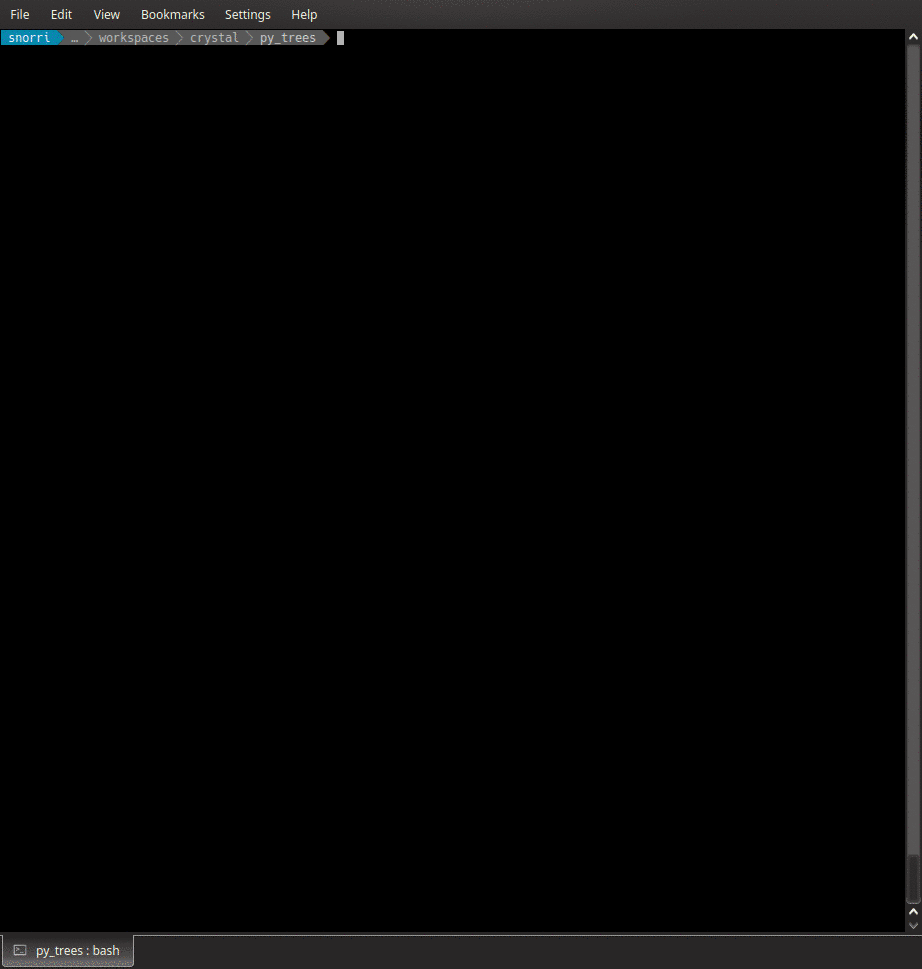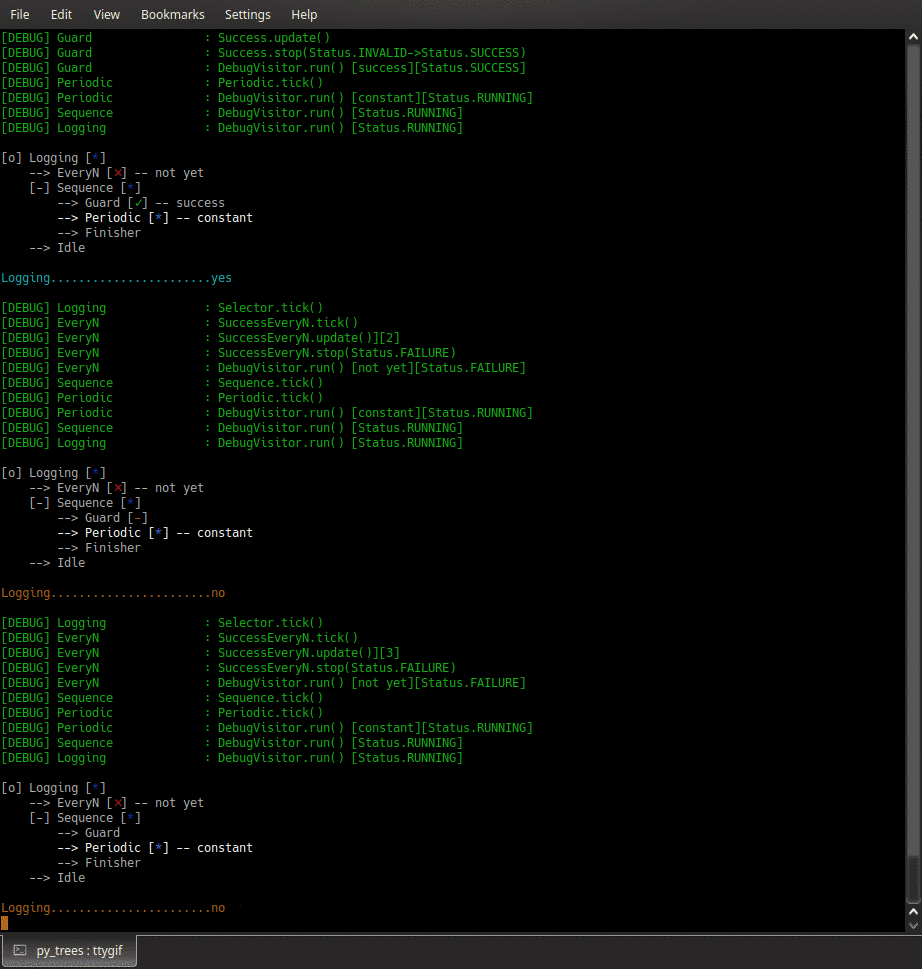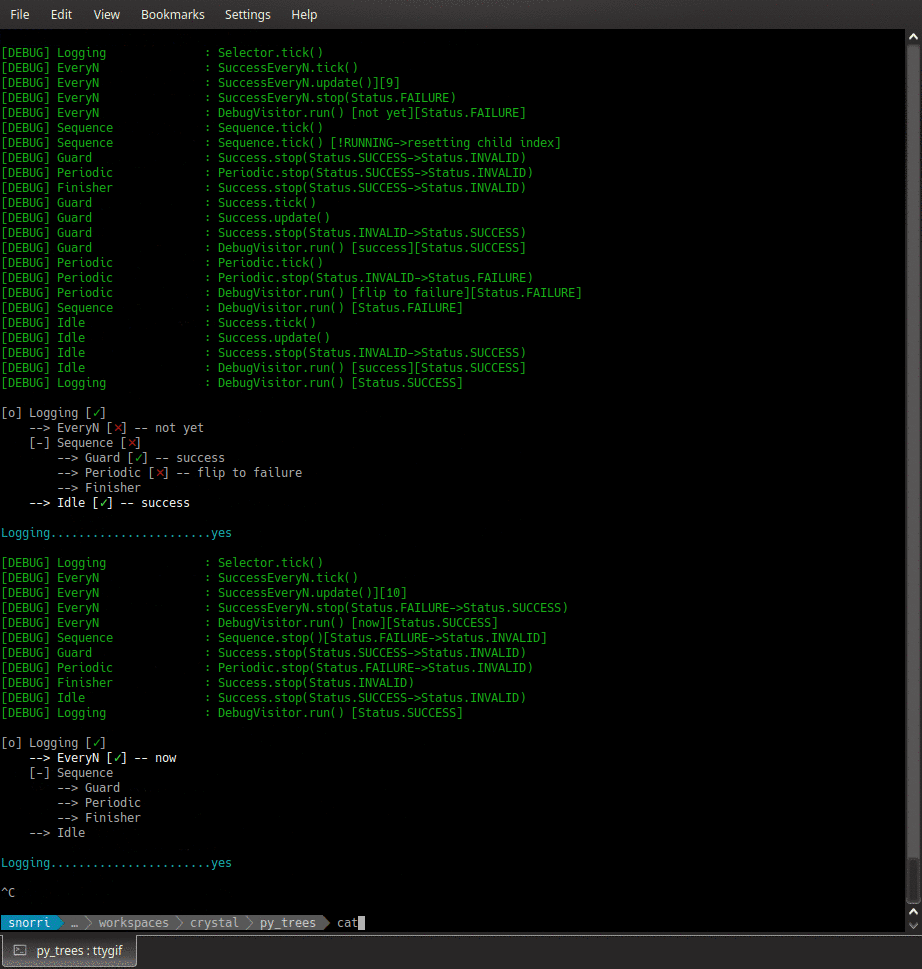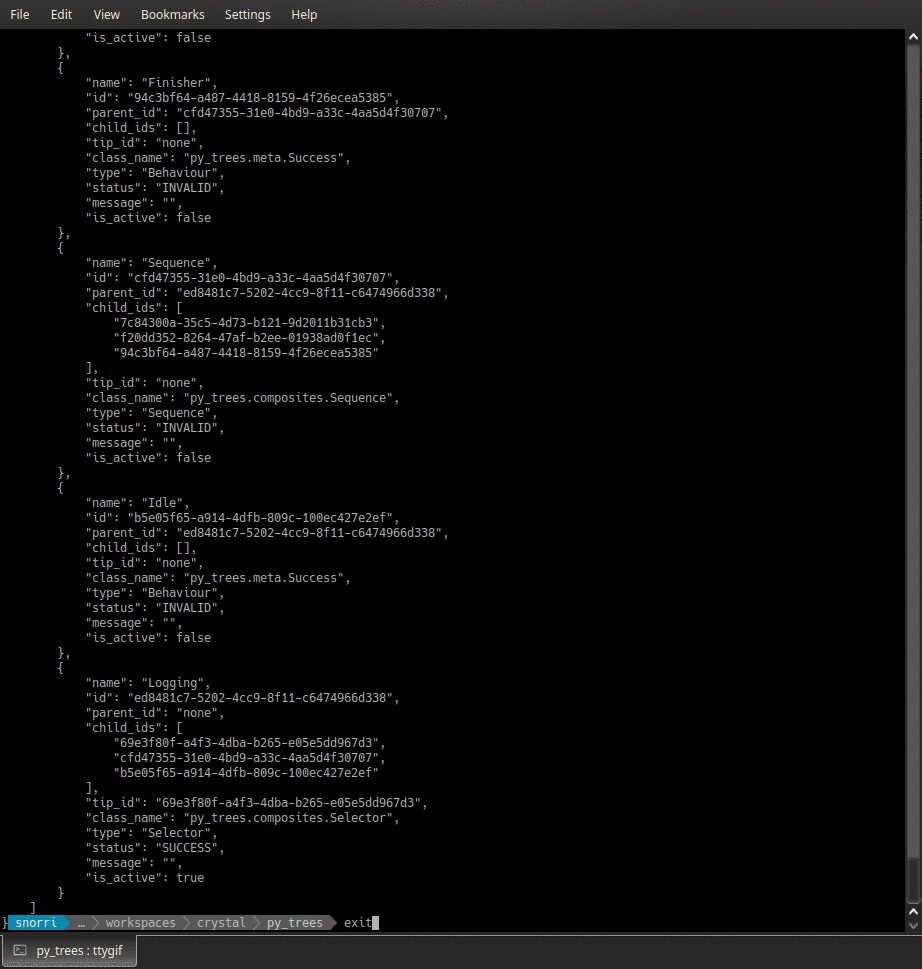
- py_trees.demos.logging.command_line_argument_parser() ArgumentParser
Process command line arguments.
- Returns:
the argument parser
- py_trees.demos.logging.create_tree() Behaviour
Create the root behaviour and it’s subtree.
- Returns:
the root behaviour
- py_trees.demos.logging.description(root: Behaviour) str
Print description and usage information about the program.
- Returns:
the program description string
- py_trees.demos.logging.epilog() str | None
Print a noodly epilog for –help.
- Returns:
the noodly message
- py_trees.demos.logging.logger(snapshot_visitor: DisplaySnapshotVisitor, behaviour_tree: BehaviourTree) None
Log the tree (relevant parts thereof) to a yaml file.
Use as a post-tick handler for a tree.
- py_trees.demos.logging.main() None
Entry point for the demo script.
py-trees-demo-selector
A py_trees demo.
- py_trees.demos.selector.command_line_argument_parser() ArgumentParser
Process command line arguments.
- Returns:
the argument parser
- py_trees.demos.selector.create_root() Behaviour
Create the root behaviour and it’s subtree.
- Returns:
the root behaviour
- py_trees.demos.selector.description() str
Print description and usage information about the program.
- Returns:
the program description string
- py_trees.demos.selector.epilog() str | None
Print a noodly epilog for –help.
- Returns:
the noodly message
- py_trees.demos.selector.main() None
Entry point for the demo script.
py-trees-demo-sequence
A py_trees demo.
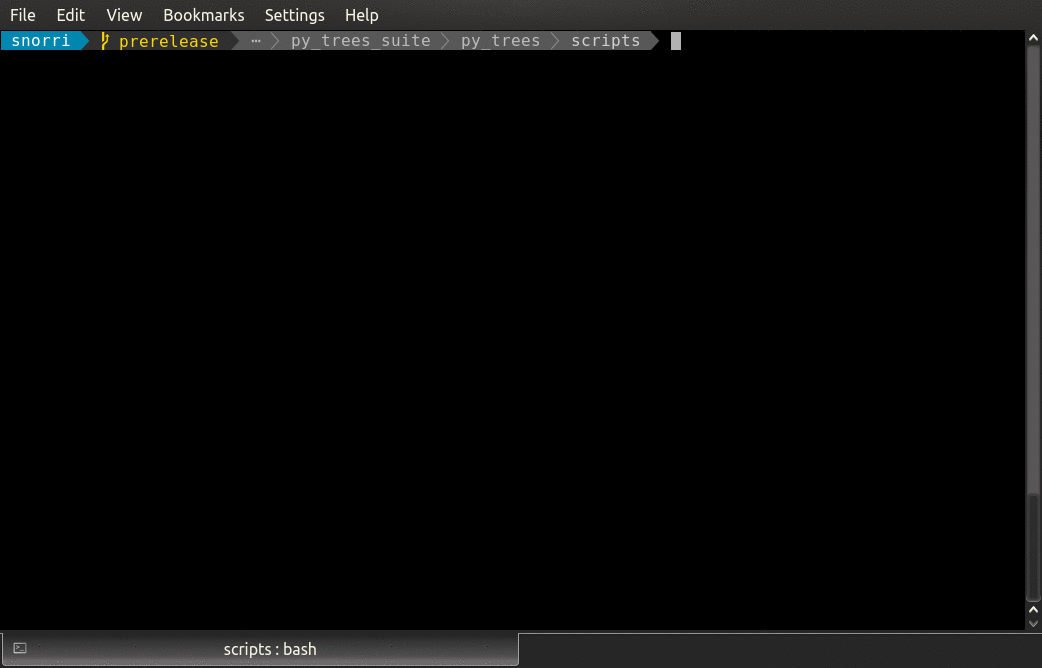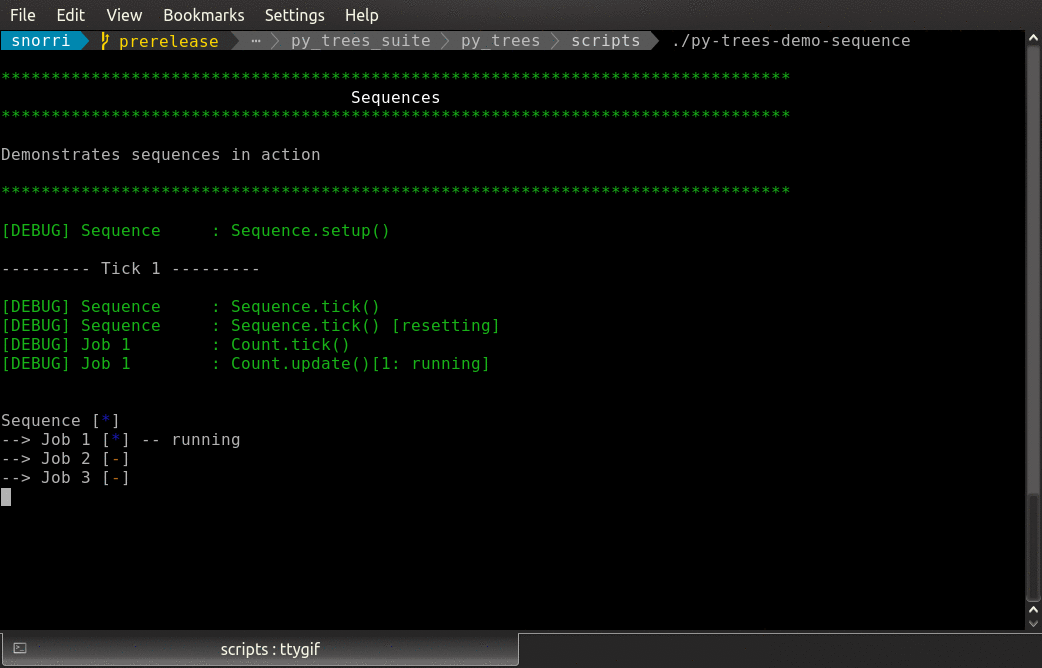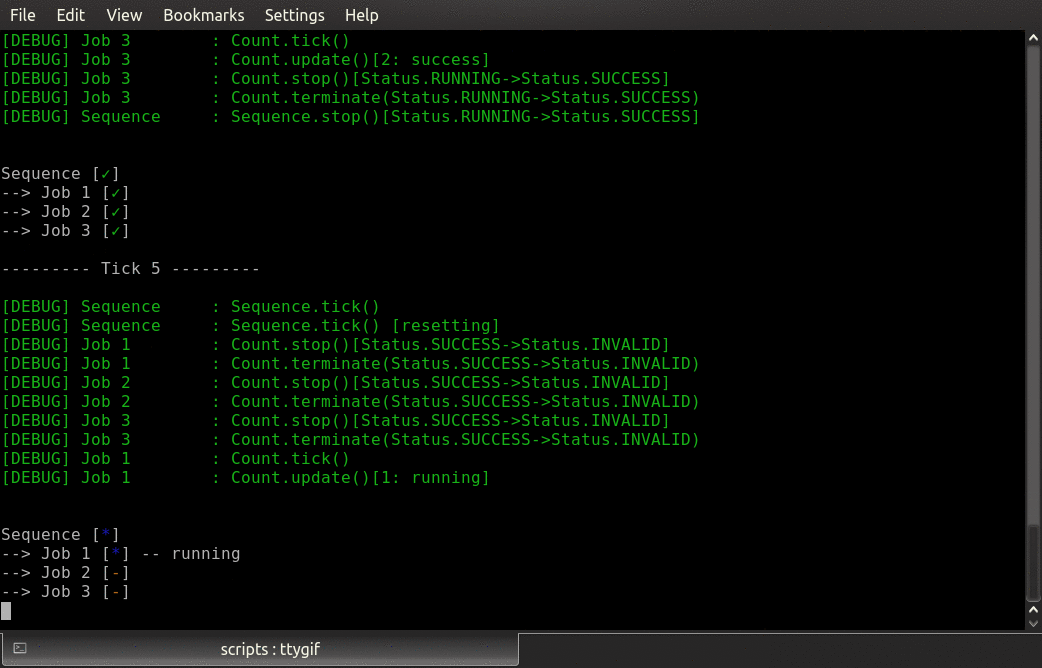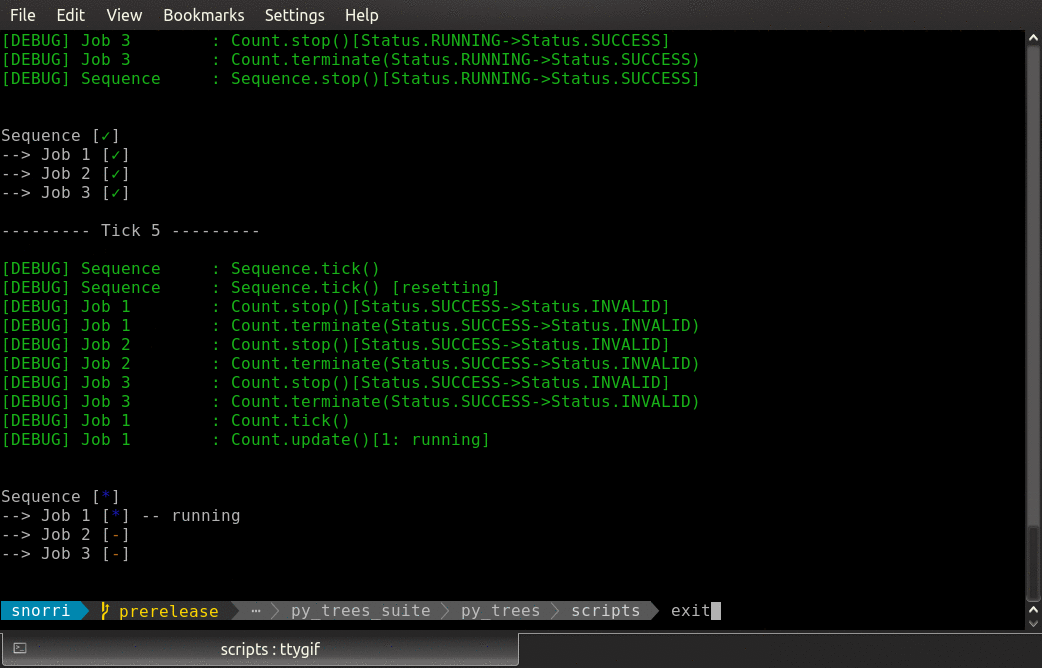
- py_trees.demos.sequence.command_line_argument_parser() ArgumentParser
Process command line arguments.
- Returns:
the argument parser
- py_trees.demos.sequence.create_root() Behaviour
Create the root behaviour and it’s subtree.
- Returns:
the root behaviour
- py_trees.demos.sequence.description() str
Print description and usage information about the program.
- Returns:
the program description string
- py_trees.demos.sequence.epilog() str | None
Print a noodly epilog for –help.
- Returns:
the noodly message
- py_trees.demos.sequence.main() None
Entry point for the demo script.
py-trees-demo-tree-stewardship
A py_trees demo.
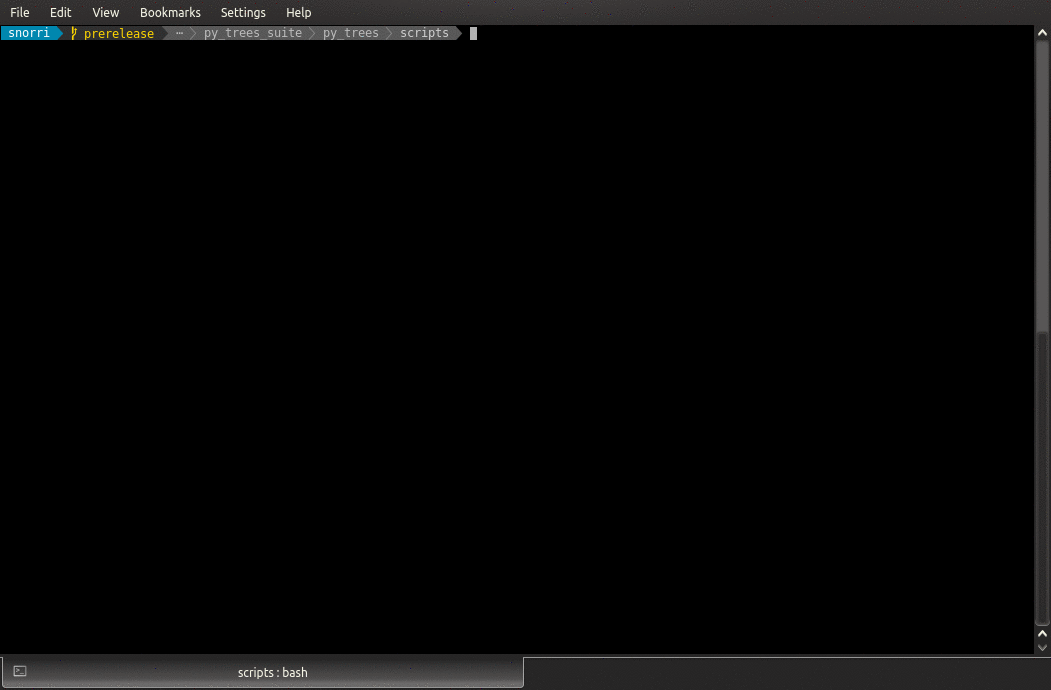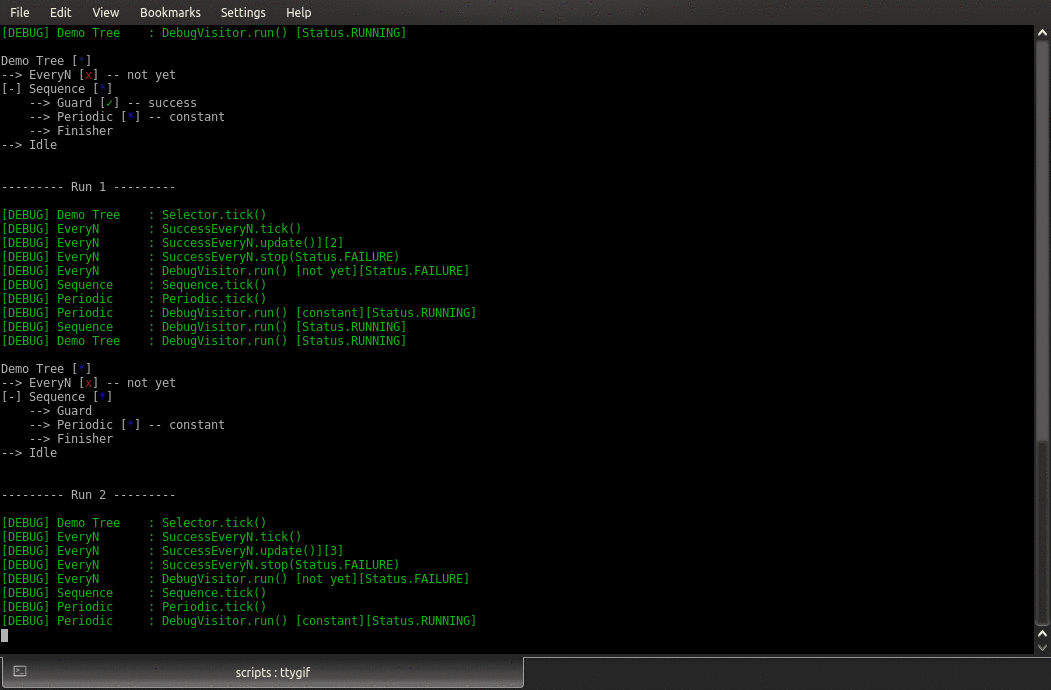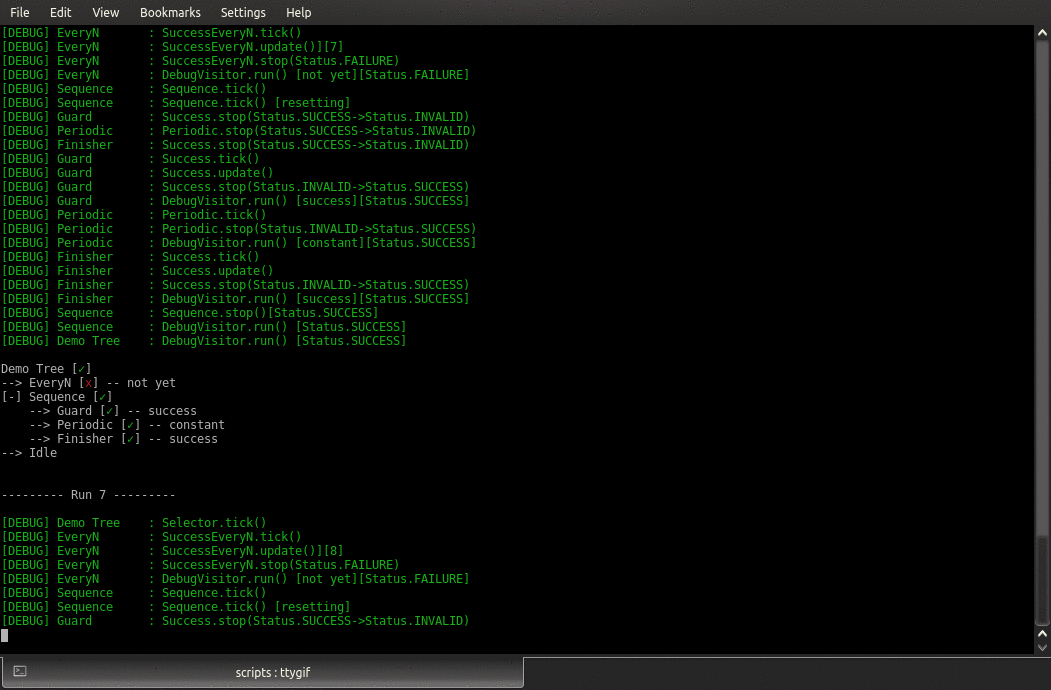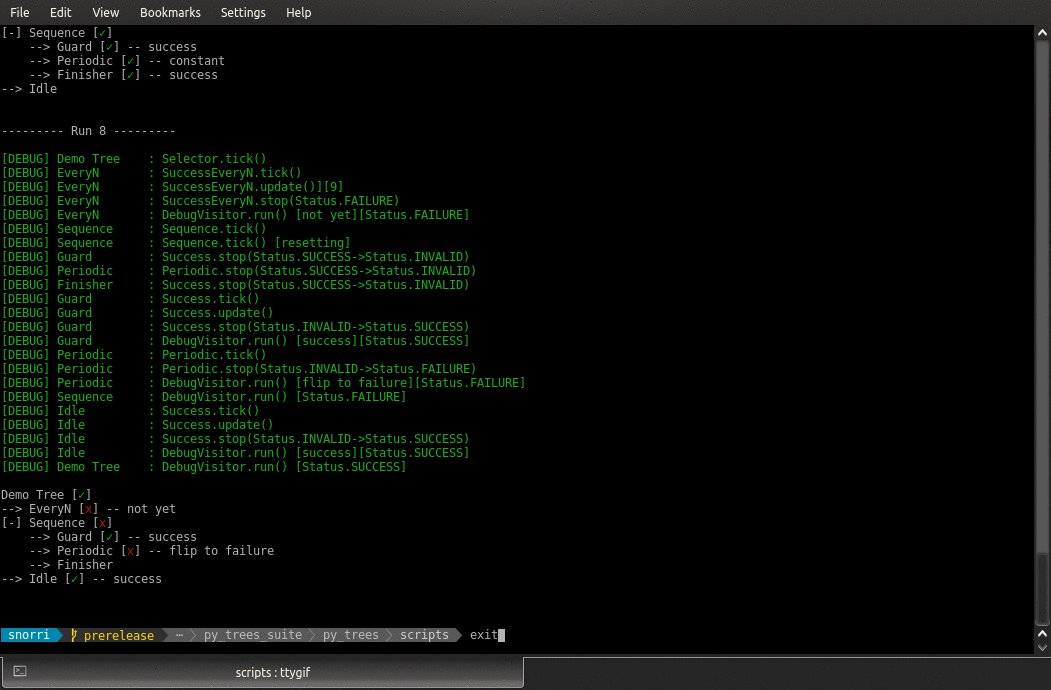
- class py_trees.demos.stewardship.Finisher
Bases:
BehaviourGathers blackboard data from other behaviours and prints a summary.
To be used at the end of the tree run.
- __init__() None
Set up the blackboard.
- class py_trees.demos.stewardship.PeriodicSuccess
Bases:
PeriodicWrite the period from
Periodicas a variable on the blackboard.
- class py_trees.demos.stewardship.SuccessEveryN
Bases:
SuccessEveryNAdd a blackboard counter to
SuccessEveryN.- __init__() None
Set up the blackboard.
- update() Status
Run the
SuccessEveryNupdate and write to blackboard.- Returns:
Returns the
StatusofSuccessEveryN
- py_trees.demos.stewardship.command_line_argument_parser() ArgumentParser
Process command line arguments.
- Returns:
the argument parser
- py_trees.demos.stewardship.create_tree() Behaviour
Create the root behaviour and it’s subtree.
- Returns:
the root behaviour
- py_trees.demos.stewardship.description() str
Print description and usage information about the program.
- Returns:
the program description string
- py_trees.demos.stewardship.epilog() str | None
Print a noodly epilog for –help.
- Returns:
the noodly message
- py_trees.demos.stewardship.main() None
Entry point for the demo script.
- py_trees.demos.stewardship.pre_tick_handler(behaviour_tree: BehaviourTree) None
Generate a simple pre-tick banner printing to stdout.
py-trees-demo-pick-up-where-you-left-off
A py_trees demo.
- py_trees.demos.pick_up_where_you_left_off.command_line_argument_parser() ArgumentParser
Process command line arguments.
- Returns:
the argument parser
- py_trees.demos.pick_up_where_you_left_off.create_root() Behaviour
Create the root behaviour and it’s subtree.
- Returns:
the root behaviour
- py_trees.demos.pick_up_where_you_left_off.description(root: Behaviour) str
Print description and usage information about the program.
- Returns:
the program description string
- py_trees.demos.pick_up_where_you_left_off.epilog() str | None
Print a noodly epilog for –help.
- Returns:
the noodly message
- py_trees.demos.pick_up_where_you_left_off.main() None
Entry point for the demo script.
- py_trees.demos.pick_up_where_you_left_off.post_tick_handler(snapshot_visitor: SnapshotVisitor, behaviour_tree: BehaviourTree) None
Print an ascii tree with the current snapshot status.
- py_trees.demos.pick_up_where_you_left_off.pre_tick_handler(behaviour_tree: BehaviourTree) None
Print a banner immediately before every tick of the tree.
- Args:
behaviour_tree (
BehaviourTree): the tree custodian